Powder
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to determine the crystallographic
structure of materials. In this technique, a powdered sample is exposed to a
beam of X-rays, and the diffracted X-rays are detected at various angles. The
resulting pattern of diffraction peaks is characteristic of the crystal
structure of the material.
The
position and intensity of the diffraction peaks in the pattern depend on the
crystal structure of the material, as well as the spacing and orientation of
the crystal planes that are responsible for diffracting the X-rays. By
analyzing the positions and intensities of the diffraction peaks, it is
possible to determine the crystal structure and orientation of the sample.
Powder
XRD is widely used in many fields, including materials science, geology,
chemistry, and physics, to identify and characterize the structures of
materials. It can be used to determine the crystal structures of various
materials, including minerals, metals, ceramics, and polymers.
Powder
XRD is a non-destructive technique, meaning that the sample remains intact
after analysis, making it particularly useful for analyzing small or precious
samples. It is also a relatively fast and cost-effective technique, which makes
it widely used in many industries and research settings.
Base
line correction
Baseline
correction is an important preprocessing step in X-ray diffraction (XRD)
analysis that is used to remove or minimize background signals in the XRD
pattern. The background signals may be due to factors such as scattering from
the sample holder, air absorption, or instrumental drift.
Baseline
correction is important because it helps to improve the accuracy of peak
identification and quantification, which is critical for understanding the
crystal structure and properties of the sample. The following are common
methods for baseline correction of XRD patterns:
- Linear interpolation:
This method involves drawing a straight line between two points on either
side of the peak, and then subtracting the line from the peak. This method
is simple and effective for removing low-frequency background signals.
- Polynomial fitting:
This method involves fitting a polynomial function to the baseline region
of the XRD pattern, and then subtracting the function from the entire
pattern. This method is more complex than linear interpolation, but can be
more effective for removing higher-frequency background signals.
- Spline fitting:
This method involves fitting a series of cubic splines to the baseline
region of the XRD pattern, and then subtracting the splines from the
entire pattern. This method can be more accurate than polynomial fitting,
especially for XRD patterns with complex background signals.
The
choice of method for baseline correction depends on the complexity of the XRD
pattern and the desired level of accuracy. It is important to carefully select
the baseline region and to avoid over-correcting the pattern, as this can lead
to the loss of important information in the XRD data.
Base
line correction using Xpert highscore Software
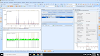
Xpert
HighScore is a software program that is commonly used for X-ray diffraction
(XRD) analysis. It provides a variety of tools and functions for analyzing XRD
data, including baseline correction. Here are the general steps to perform
baseline correction of an XRD pattern using Xpert HighScore:
- Open the XRD data file in Xpert
HighScore.
- Select the region of the XRD pattern
where the baseline needs to be corrected. This is typically the region
around the peaks of interest.
- Go to the "Tools" menu and
select "Baseline Correction."
- Choose the method of baseline
correction from the available options, such as linear interpolation,
polynomial fitting, or spline fitting.
- Adjust the parameters of the baseline
correction method as needed, such as the order of the polynomial function
or the number of splines.
- Apply the baseline correction to the
XRD pattern by clicking on the "Apply" button.
- Review the corrected XRD pattern and
adjust the baseline correction parameters as needed until the background
signal is minimized and the peaks of interest are clearly visible.
- Save the corrected XRD pattern as a
new file or overwrite the original file.
It is important to note that the specific steps for baseline correction may vary depending on the version of Xpert HighScore software and the complexity of the XRD pattern. It is recommended to refer to the user manual or seek guidance from an expert if necessary.



0 Comments